

They’re up to 90% cheaper because you’re occupying this spare capacity that’s otherwise just losing money. If you’re just testing AWS and don’t want to commit, this is the way to go.Ī company of AWS’s scale will always have space computing capacity available. When you use on-demand pricing, you pay by the hour or by the second without pre-paying for anything.
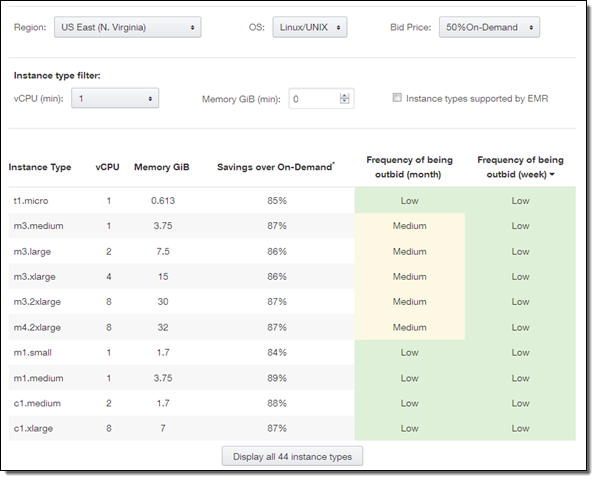
We already covered this in the beginning. Also, AWS offers the most variety in terms of pricing plans for EC2. I’ll be talking about pricing plans in the context of EC2 since it’s the service that everyone uses. Now, let’s look at AWS’s Pricing Plans before jumping into the examples.

I recommend getting familiar with the Pricing Calculator before that happens. It’s not the most exciting activity you can do, but it can save you both money and headaches in the long run.Ī quick sidenote – AWS has released a different Pricing Calculator that will completely replace the Simple Monthly Calculator. Finally, get in the habit of analyzing your bills. Also, run a few tests to see what works and what doesn’t. AWS has a bunch of tools for the job like the Simple Monthly Calculator. Always jot down some estimates before you start using a service. I know new tech is exciting but take your time and get a good understanding of how pricing works for specific services.Įstimate, test, analyze. It’s long and boring and you still shouldn’t skip reading it. AWS releases detailed documentation for this purpose. Check the price tag of each service and especially everything written in a smaller font. If this principle doesn’t hold true for a specific service, you’re probably using it wrong. Making a commitment is the way to get substantial cost-savings in AWS. If you want to save money, this is how you do it. The more you commit, the less you should pay. Use on-demand pricing only when you really need to. Price has been the main selling point for all cloud providers. It’s easy to get fooled into thinking the cloud is cheap by design. Principles might be a strong word since this is just common sense but bear with me. That said, let’s set a few principles you should follow when getting started. You’d be surprised by how many people skip this part and rack up horrendous bills as a result. Now, this all seems pretty easy to digest. As you scale, you can reduce this price even more.Ĭheck out the video below if you want more details. For example, the more data you upload to S3, the less you pay per GB. Some AWS services are tiered based on your usage. You can pay nothing upfront (most expensive), partially upfront (less expensive), or all upfront (least expensive) for your reservation. That way, you’re committed to working with AWS and get a price reduction in return. You can also request specific services in advance. There’s no buying physical servers and wondering what to do with them in case you overprovisioned. At the end of the month, you pay for what you’ve used. You use resources only when you need them. This is what pops into your head when you think of the cloud. I want to quickly run through them and suggest a few common sense principles. If you go to the AWS pricing page, you’ll see that there are 3 ways to pay for the resources you use. If you’re already spending $100 million a year on AWS (Hi, Lyft), this article might not be for you.īut if you’re just starting out and you’ve managed to spend your entire monthly budget in a day (Hi, everyone using Lambda for the first time), keep reading. I’ll also do an overview of the different pricing models, along with some examples from EC2, S3 and Lambda. In this article, I’ll go over the most important pricing principles that all AWS users need to know.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
